Distributed Systems Practice Notes
Docker and Containers - DevOps Beginner Lab
October 23, 2018
In this lab you will run a popular, free, lightweight container and explore the basics of how containers work, how the Docker Engine executes and isolates containers from each other.
Highlighted Concepts
- Docker engine
- Containers & images
- Image registries and Docker Store (AKA Docker Hub)
- Container isolation
Official Links
Lab: DevOps Docker Beginners Guide
Prerequisites
- Docker Id to access the online classroom
Operations
1. Hello World
- Run in terminal
docker container run hello-world- First you get an error for there is no image named hello-world on your local machine.
- Then Docker engine looks it up in Docker image registry (Docker Store), downloads and runs it.
2. Docker Images
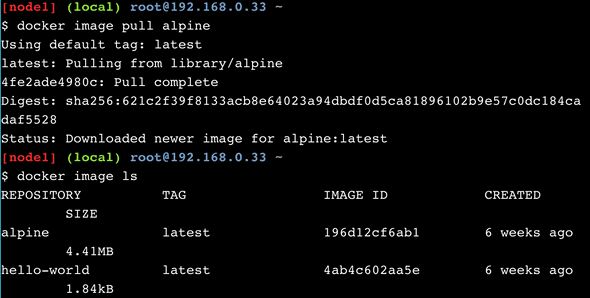
- Run in terminal to pull Alpine Linux image from Docker image registry (Docker Store)
docker image pull alpine- See a list of images on local host, Alpine Linux is on the list
docker image ls-
Run a container on Alpine image
docker container run alpine ls -lWhen you call run, the Docker client finds the image (alpine in this case), creates the container and then runs a command in that container. When you run docker container run alpine, you provided a command (ls -l), so Docker executed this command inside the container for which you saw the directory listing. After the ls command finished, the container shut down.
Then try
docker container run alpine echo "hello from alpine"and
docker container run alpine /bin/shThe shell starts and closes in Alpine, to interact with the Alpine shell, run
docker container run -it alpine /bin/sh- To see the containers that are currently running,
docker container ls- To see the containers that you have run,
docker container ls -a3. Container Isolation
-
Each docker container run command creates an isolated container, which is listed by command docker container ls -a
-
For example, create a text file in one container
docker container run -it alpine /bin/ash
echo "hello world" > hello.txt
ls- Then use command ls to see the file
docker container run alpine ls-
The text file is missing because the command ls is run in another container (isolation), this feature not only for security, but to test the effects of making application changes. Isolation allows users to quickly create separate, isolated test copies of an application or service and have them run side-by-side without interfering with one another.
-
To get back to the container that has my ‘hello.txt’ file, first get the Container ID
docker container ls -a- Then start the container with the specific id
docker container start <container ID>- Use exec to run ls command in that container, you will see the text file
docker container exec <container ID> ls
Written by Warren who studies distributed systems at George Washington University. You might wanna follow him on Github